Appearance
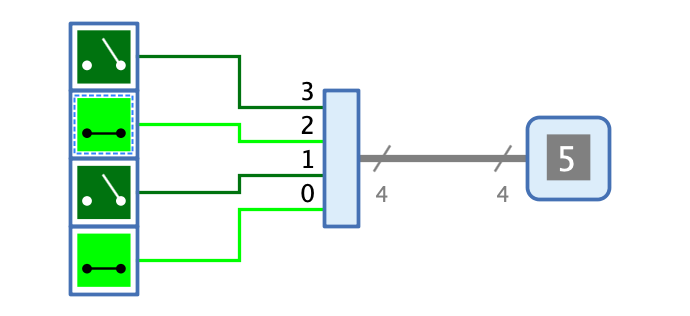
Behavior
The combiner can be used to combine the signals of several wire bundles (or single wires) onto a wire bundle that contains more bits than the incoming wire bundles.
The degree of combining is limited in that only integer dividers of the bit width of the output wire bundle are possible. For example, an 8-bit wire bundle can only be combined as follows:
-
2: The combiner has 2 inputs of 4 bits each
-
4: The combiner has 4 inputs of 2 bits each
-
8: The combiner has 8 inputs of 1 bit each
The combiner is uni-directional; it only forwards signals from the input pins to its output pin. See bi-directional splitter for a bi-directional version.
For technical reasons, the current version of Antares has the restriction that the properties "Bit Width" and "Fan Out" can no longer be changed if pins are already connected to wires. Perhaps a future version will at least allow to increase the number of bits without having to disconnect existing wire connections beforehand.
Pins
- Output
-
The combiner has a single output whose bit width is determined by the property "Bit Width".
- Inputs
-
The number of inputs of the combiner is determined by the property "Fan Out". Each input has the bit width "Bit Width" / "Fan Out" and carries during simulation those bits of the input signal which correspond to the index of the input. For a combiner with 8-bit output and a fan out of 2, input 0 carries bits 0..3 and input 1 carries bits 4..7.
Properties
- Orientation
-
The direction in which the output pin points.
- Bit Width
-
Determines the bit width of the output.
- Fan Out
-
Specifies the number of inputs. The bit width of each input is defined by the formula Bit Width" / "Fan Out". Should maybe more accurately be called "Fan In".
- Position Bit 0
-
This property can be used to determine the position of the inputs within the combiner.
-
Right: The input carrying bit 0 is located on the right side of the combiner from the point of view of the signal outgoing at the output.
-
Left: The input carrying the bit 0 is on the left side of the combiner from the point of view of the output signal.
-
- Representation
-
The way in which the value of the output signal is represented, which is used in signal flow animation, for example. Binary and hexadecimal representation are available.